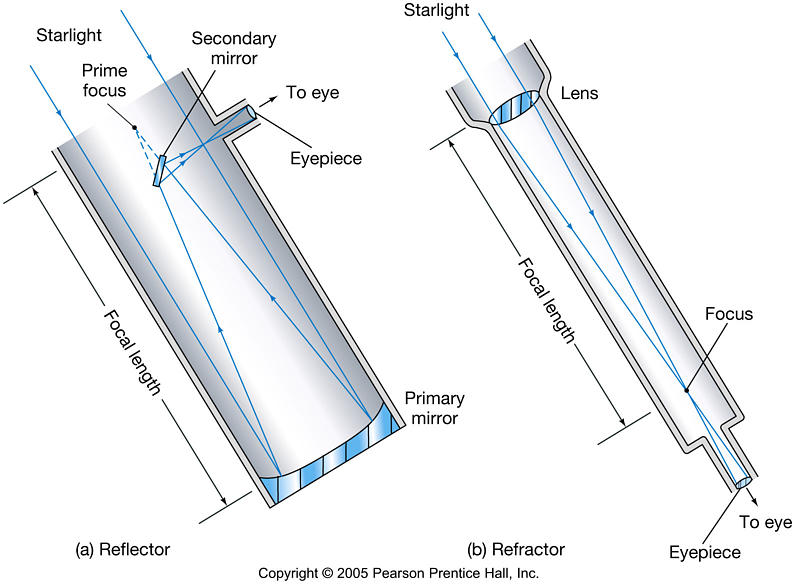
Refraction
·
Forms an image using a lens
·
Light converges to from an image at the focus
or focal point
·
Telescope use an objective lens to form a primary image
·
There are major limitations:
o
The scope has to be long and hold a large/heavy
lens
o
Correct shape of the lens is crucial and must
be perfect at all times
o
The support of the lens is on the edge of lens and can cause it to sag
o
Lenses suffer from CHROMATIC ABERRATION
§ Refraction
is dispersive
§ Chromatic
Aberration occurs when the dispersive nature of refraction blurs the original
image
·
Would be okay for close objects, but not ideal
from distance viewing
 |
| Refracting Telescope |
Reflecting
· Uses a series of mirrors to transmit image to a
focal point
·
Law of Reflection: Angle of incidence is equal
to the angle of reflection
·
Must be CONCAVE mirrors
o
Receives light from range view
·
Telescope uses a primary mirror to form primary image
o
Kind of like WYSIWYG
·
Advantages of using this scope
o
Use of greater diameter which means more light
can be collected
§ More
light means more vivid, detailed image
o
One perfect reflecting surface
o
Supported anywhere behind the mirror
o
NO Chromatic Aberration
Diffraction
·
The bending of light around corners of edges
·
Longer wavelengths
of light bend more than shorter wavelengths which results in issues for larger
diffracting models
o
Splits light into its component wavelengths
(the color spectrum)
o
Causes heavy dispersion

No comments:
Post a Comment